
If we talk about video, the connector par excellence today is HDMI. When a few years ago we talked about the euroconnector and all its pins, luckily today, connecting a device has been limited to placing a small connector that is easy to connect. It is HDMI, a port that hides a lot of standards that you should know.
All types of HDMI that exist
Although the connector may be identical in shape on many devices, it doesn't mean that they all work the same. The port has evolved over the years, gradually improving its speed and adding additional features. The surprising thing is that there are cables designed for special functions, so the HDMI standard organization has listed the following categories.
HDMI cable types

The first thing you will have to do is find the cable that best suits your needs. Not all HDMI cables are the same, and not only because of their connector, but also because of the quality of the cables inside. These are all the types of HDMI cables that exist:
- Standard: Basically designed for use in consumer electronics with resolutions ranging between 720p and 1080i. It is quite rare to find these types of cables today because they have been replaced by the new Hight Speed ones.
- Standard with Ethernet: Model similar to the standard with the peculiarity of including a channel specially dedicated to network data transfer.
- Standard Automotive: Cable specially designed for use in the automotive sector. This type of cable supports higher power signals, withstands vibrations and its connector is usually an HDMI Type E with a safety clamp.
- High Speed: It is the current model most used and distributed throughout the world. It introduces the possibility of handling 1080p content and reaching 4K resolutions at 30 images per second, as well as being compatible with 3D format.
- High Speed with Ethernet: Same cable as above with the introduction of an Ethernet channel to communicate devices through the local network.
- High Speed Automotive: Cable designed for use in the automotive sector and capable of handling 1080p and 4K/30p resolution.
- Premium High Speed: One more speed jump. With this type of cables we will be able to reach 4K resolutions at 60 images per second, transmitting a video signal with HDR and including color space such as BT.2020.
- Ultra High Speed: It is the currently recommended cable for use in the most modern and up-to-date devices. The reason is that it supports the HDMI 2.1 specification capable of moving images in 8K resolution at 60 images per second and 4K at 120 images per second. The bandwidth of this cable reaches 48 Gbps, and is also capable of resisting interference from nearby wireless devices.
Types of HDMI connections
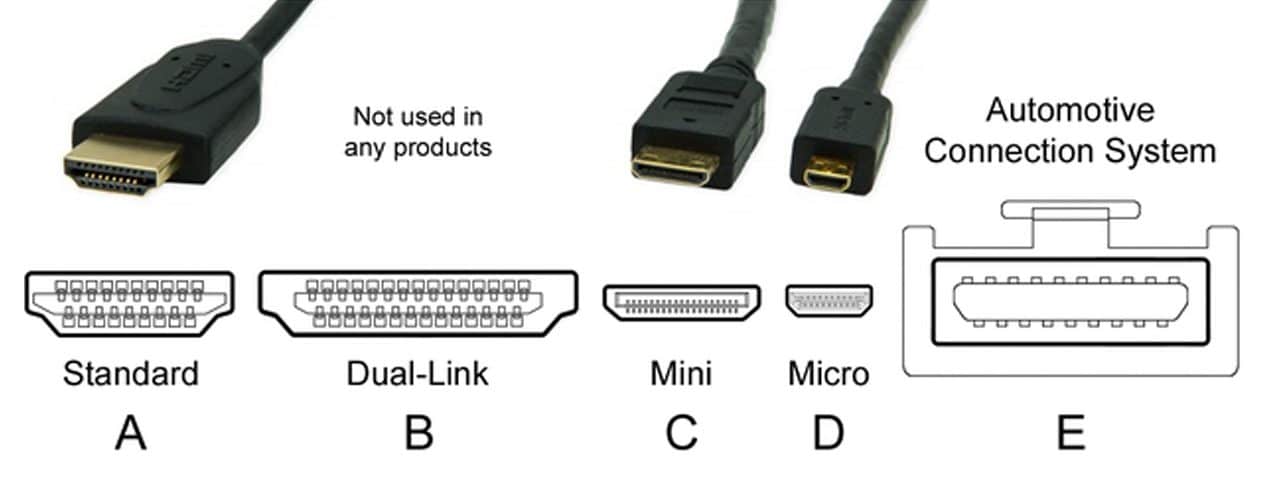
HDMI connectors are easily recognizable, but there are some variants that you might miss. We leave you with a list of the different connectors that exist today with the HDMI format:
- Type A: It is the usual HDMI connector, the one we will find in most devices. Also known as Standard, it is the connector that has given life to HDMI since its inception and the one that everyone recognizes as such. It consists of a total of 19 pins.
- Type B: It is a Dual-Link connector that has not been used much and is now almost gone. There are no commercial products that offer it, so it will be difficult to find it. It features an extended 29-pin configuration.
- Type C: It is the HDMI Mini, smaller and more compact than the original, usually found in cameras and small devices. It is characterized by being a fairly flat and elongated connector. 19 connection pins.
- Type D: The micro HDMI. The minimal expression of the 19-pin connector. Used in small and very small devices. It is the one offered in the Raspberry Pi 4.
- Type E: Special connector used in the automobile industry. It is a larger connector and with security measures to avoid disconnections.
The versions of HDMI
Taking into account the evolution of the manufacturing quality of the cables, the HDMI standard has been increasing in level to gradually offer better features in terms of image quality and extra functions. Thus, as the years passed, the HDMI organization published new specifications with which to guarantee performance depending on the type of cable and connector.
The different versions that we can find in the market are the following:
HDMI 1.0
- HDMI 1.0: Released in 2002, this specification is the basic one for HDMI. It was born to unify audio and video in the same cable based on the now extinct DVI.
- HDMI 1.1: It was a minor revision, since it simply included support for DVD-Audio
HDMI 1.2
- HDMI 1.2: It arrived in 2005 and added the One Bit Audio option included in Super Audio CDs. It included new formats such as 720p at 100 Hz and 720p at 120 HZ.
- HDMI 1.2: A small but important update that was released after completing the Consumer Electronic Control (CEC) requirements, which allowed you to take control of HDMI-connected devices with a single remote control.
HDMI 1.3
- HDMI 1.3: Released in 2006, add new video bandwidth at 8,16 Gbit/s with resolutions of 1.920 x 1.080 pixels at 120 Hz or 2.560 x 1.440 pixels at 60 Hz. Dolby TrueHD support included for the first time and DTS HD-Master Audio to play those codecs on external AV amplifiers.
- HDMI 1.3: Minor update that included modifications to the Type C connector and some changes to the CEC, such as time control and audio-related commands.
HDMI 1.4
- HDMI 1.4: It arrives in 2009 to increase the bandwidth with which to reach resolutions of 4.096 x 2.160 pixels at 24 Hz, 3.840 x 2.160 at 24, 25 and 30 Hz and 1.920 x 1080 pixels at 120 Hz. It is the first contact with the 4K, and launches the Ethernet channel, being able to include a 100 Mbit/s Ethernet connection between two HDMI devices. ARC, 3D over HDMI and a new micro HDMI connector are introduced.
- HDMI 1.4: Designed to boost the 3D video market that began to grow in 2010. It requires screens with 3D format.
- HDMI 1.4b: Launched to clarify some details of the previous version. It is the latest specification licensed by HDMI LLC.

HDMI 2.0
- HDMI 2.0: In 2014 comes the great leap in quality, commonly known as HDMI UHD. The bandwidth grows to 14,4 Gbit/s for video, being able to carry video in 4K format at 60 images per second with 24 bits per pixel in color depth. It includes up to 32 audio channels, a 21:9 aspect ratio, dynamic A/V synchronization, and many other features focused on modern video.
- HDMI 2.0: Adds HDR video support with metadata.
- HDMI 2.0b: Includes support for HDR10 and HLG standards.
HDMI 2.1
It is the most current and complete standard that exists today. It was launched at the end of 2017, and allows you to jump to 8K resolution at 120 images per second with its 48 Gbit/s bandwidth. It also supports 4K at 120 images per second. In order to enjoy all the features of this standard, it is necessary to use the Ultra High Speed cable, added during this generation.
Technically, this standard can support 10K resolutions at 120 Hz. Regarding the rest of the features, HDMI 2.1 sets the bar quite high: dynamic HDR with scene-by-scene or image-by-image metadata control, High Speed Refresh (HFR), eARC and technologies such as Variable Refresh Rate (VRR), Quick Signal Change (QMS) or Quick Frame Transport (QFT). It also includes Automatic Low Latency Mode (ALLM).
However, with the HDMI 2.1 standard, many manufacturers have played a little dirty to misinform and make sales by selling what they don't have. HDMI 2.1 is a standard that can support a whole number of specifications. This standard encompasses the entirety of the previous standard and introduces new improvements. The problem is that many manufacturers have used this small detail to bring out features that their televisions do not have. Just because a TV supports HDMI 2.1 doesn't mean it has all of its features. This problem has been aggravated a bit because not even HDMI.org has brought order, leaving it to be read between the lines that it must be the client himself who has to go to the specifications of a device and see what technical characteristics of HDMI 2.1 are supported on the device. equipment. This obviously seems like a mistake to us, and HDMI.org should be putting the order in place to make their standard more and more easy to understand, rather than the other way around. Therefore, the only advice we can give you so that you are prepared is that you know the specifications you need well and check on the HDMI 2.1 monitor or television that you are going to buy if they are included or not.
Differences between specifications
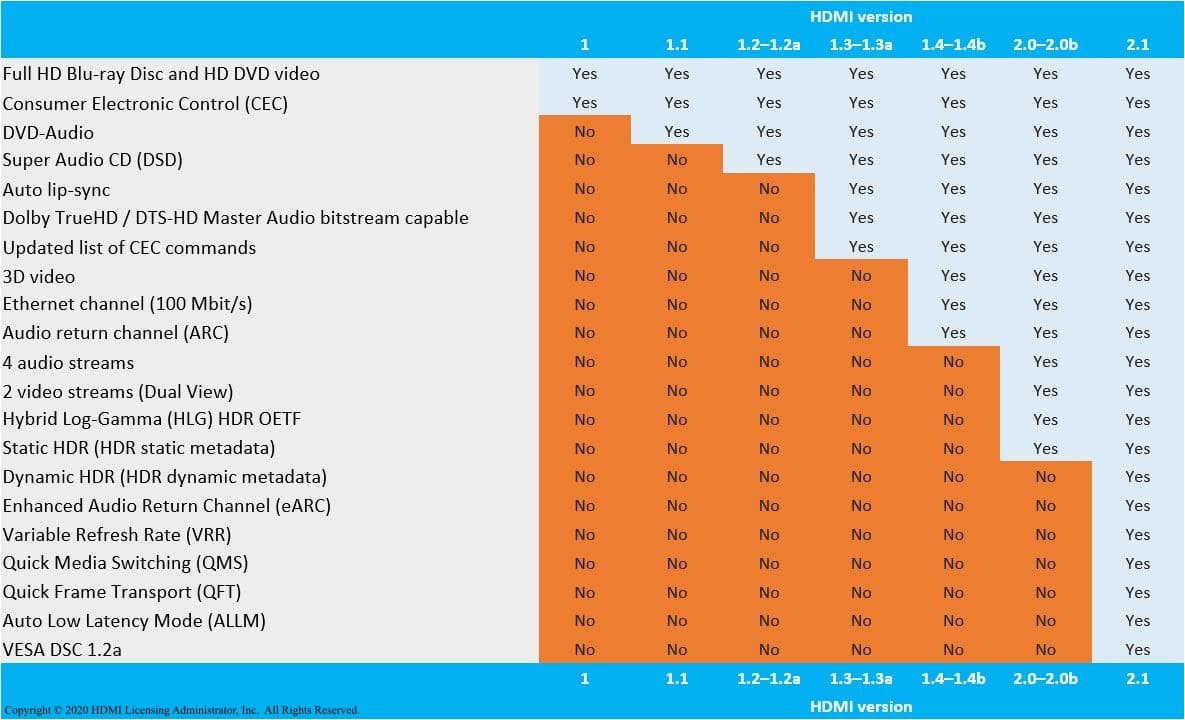
In this table you can see the different current technologies and which HDMI standards support them. As we told you, HDMI 2.1 supports each and every one of the features of its predecessors. That is why this standard has generated so much confusion.
To give you an example, it is entirely possible that you buy a TV with HDMI 2.1 and it does not support VRR or ALLM. If you are interested in these two features - which are almost essential to get the most out of video games - you will have to look for devices with HDMI 2.1 that also support those two features. A mess, but that's how they've made the standard.
HDMI for PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X
Taking into account all the terms that we have previously reviewed and the specifications that each of the standards offers, you should now know that for the new consoles to work correctly on modern screens, you must use an HDMI 2.1 cable to enjoy technologies such as VRR and ALLM, so make sure to choose the right cable if you want to get the best video quality on the new generation of consoles.
What cable do I need to see from my clu. Samsung j7 to a tv. lcd thank you